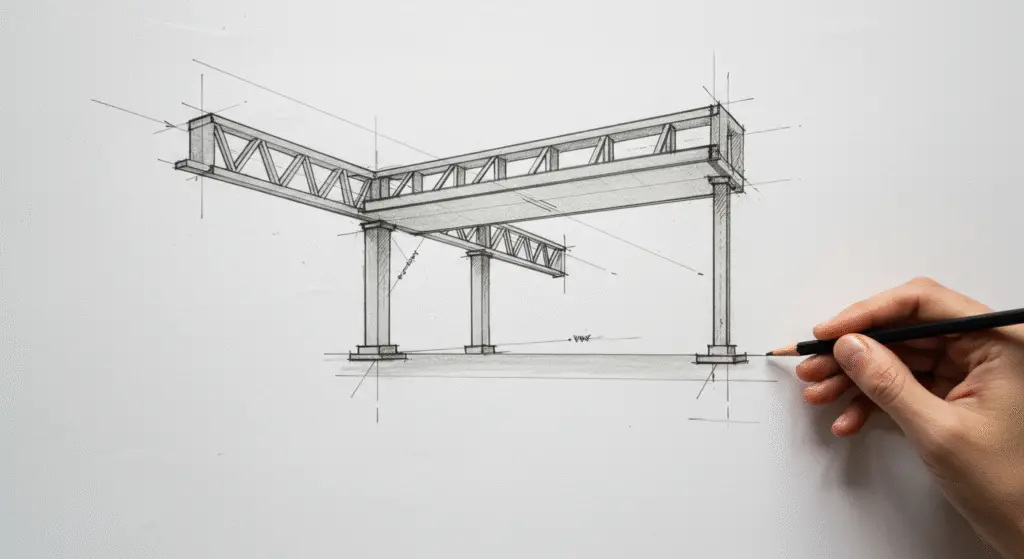
The Three Main Types of Technical Drawing
Introduction
Technical drawing is a fundamental skill in various engineering and design disciplines, requiring the creation of precise and detailed technical drawings. These drawings serve as visual representations of designs, plans, and specifications, essential for conveying ideas and guiding the manufacturing and construction processes. To achieve the necessary precision and accuracy, technical drawings are categorized into different types based on their purpose and application. This guide explores the three main types of technical drawing, highlighting their characteristics, applications, and the critical role they play in producing high-quality technical documentation.
1. Presentation Drawings
- Definition: Presentation drawings are technical drawings that are used to communicate the final design of a product or structure. They are intended to provide a clear and visually appealing representation of the design, often used in proposals, marketing materials, and client presentations.
- Purpose: The primary purpose of presentation drawings is to convey the design in a way that is easily understood by non-technical stakeholders. These drawings are used to showcase the aesthetic and functional aspects of the design.
- Key Elements:
- Visual Appeal: Presentation drawings are often rendered with shading, textures, and other visual effects to make the design more appealing.
- Simplicity: These drawings are simplified to focus on the key features of the design, avoiding unnecessary details.
- Clarity: Presentation drawings are designed to be clear and easy to understand, ensuring that the design is communicated effectively.
- Applications: Presentation drawings are used in various fields, including architecture, product design, and engineering. They are particularly useful in the early stages of a project to convey the design concept to clients or stakeholders.
- Examples: Architectural renderings, product design visuals, and conceptual sketches.
2. Construction Drawings
- Definition: Construction drawings are technical drawings that provide detailed instructions for the construction of a product or structure. These drawings are used by contractors, builders, and manufacturers to guide the actual construction process.
- Purpose: The primary purpose of construction drawings is to provide precise instructions for the construction of the design. These drawings include all the necessary details, dimensions, and specifications required to bring the design to life.
- Key Elements:
- Precision: Construction drawings must be highly precise, with accurate measurements and detailed specifications.
- Compliance: These drawings must comply with relevant building codes, standards, and regulations.
- Completeness: Construction drawings should include all the necessary information required for the construction process, leaving no room for ambiguity.
- Applications: Construction drawings are used in various fields, including architecture, civil engineering, and manufacturing. They are essential for ensuring that the construction process is carried out accurately and efficiently.
- Examples: Architectural blueprints, engineering schematics, and manufacturing plans.
3. Working Drawings
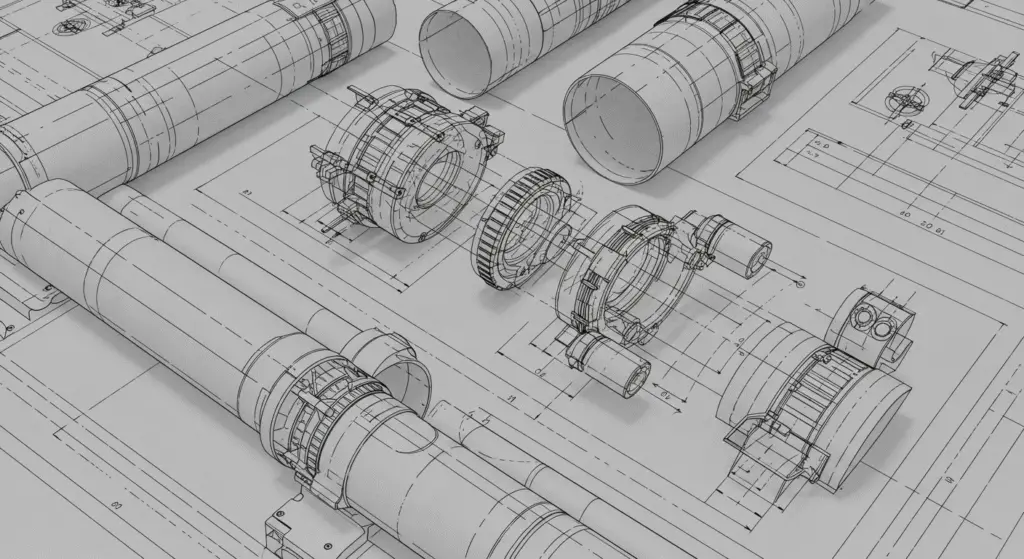
- Definition: Working drawings are technical drawings that provide detailed instructions for the fabrication or assembly of a product or structure. These drawings are used by manufacturers, fabricators, and assembly line workers to guide the production process.
- Purpose: The primary purpose of working drawings is to provide detailed instructions for the fabrication or assembly of the design. These drawings include all the necessary details, dimensions, and specifications required to produce the final product.
- Key Elements:
- Detail: Working drawings must include all the necessary details required for the production process, including dimensions, tolerances, and material specifications.
- Accuracy: These drawings must be highly accurate, with precise measurements and specifications.
- Clarity: Working drawings should be clear and easy to understand, ensuring that the production process is carried out efficiently and effectively.
- Applications: Working drawings are used in various fields, including manufacturing, mechanical engineering, and aerospace engineering. They are essential for ensuring that the production process is carried out accurately and efficiently.
- Examples: Machine drawings, assembly drawings, and fabrication plans.
Importance of Understanding the Types of Technical Drawing
Understanding the different types of technical drawing is essential for engineers, designers, and technicians. Each type of drawing serves a specific purpose, and the effective use of these drawings is critical to the success of engineering and design projects. By understanding the characteristics, applications, and requirements of each type of drawing, professionals can create high-quality technical documentation that meets the needs of stakeholders.
Tools and Software Used in Technical Drawing
The creation of technical drawings requires the use of specialized tools and software. These tools enable professionals to create precise and accurate drawings, ensuring that the design is represented clearly and effectively. Some of the commonly used tools and software in technical drawing include:
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD) Software: CAD software is widely used in technical drawing to create detailed 2D and 3D models. Popular CAD software includes AutoCAD, SolidWorks, and Revit.
- Graphics Tablets: Graphics tablets are used to create freehand sketches and modify digital drawings. They provide a natural drawing experience, allowing professionals to create precise and accurate drawings.
- 3D Scanners and Printers: 3D scanners and printers are used to create detailed 3D models of objects and environments. These tools are essential for rapid prototyping and design visualization.
- Protractors and Triangles: Protractors and triangles are used to measure and draw precise angles and lines. These tools are essential for maintaining accuracy in technical drawing.
- Scale Rules: Scale rules are used to measure distances and convert them into proportional representations. These tools are essential for maintaining scale in technical drawings.
Best Practices in Technical Drawing
The creation of high-quality technical drawings requires the use of best practices. These practices ensure that drawings are precise, accurate, and easy to understand. Some of the best practices in technical drawing include:
- Precision: Technical drawings must be highly precise, with accurate measurements and detailed specifications.
- Clarity: Drawings should be clear and easy to understand, avoiding unnecessary complexity and ambiguity.
- Consistency: Consistency is essential in technical drawing, ensuring that all elements of the drawing are represented in a uniform manner.
- Use of Standards: Technical drawings should comply with relevant standards and conventions, ensuring that they are universally understood.
- Regular Practice: Regular practice is essential to master the skills required in technical drawing. The more you practice, the more comfortable and proficient you will become in creating high-quality technical drawings.
Case Studies
Examining real-world examples of technical drawings can provide valuable insights into the practical application of these drawings. For instance, architectural plans for a residential building might use presentation drawings to convey the design concept to clients, construction drawings to guide the building process, and working drawings to provide detailed instructions for the fabrication of components.
Emerging Trends in Technical Drawing
The field of technical drawing is continually evolving, with emerging technologies offering new possibilities for improving the design and manufacturing processes. Some of the emerging trends in technical drawing include:
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): AR and VR technologies are being used to visualize and interact with digital models, enhancing the design and collaboration process.
- Building Information Modeling (BIM): BIM is a digital representation of physical and functional characteristics of a building. It is being used to create detailed models of buildings and infrastructure, facilitating collaboration and improving the efficiency of the construction process.
- 3D Printing: 3D printing is being used to create physical prototypes of designs, allowing for the visualization and testing of products before they are manufactured.
Conclusion
The three main types of technical drawing—presentation drawings, construction drawings, and working drawings—are essential for conveying design ideas, guiding the construction process, and providing detailed instructions for the fabrication or assembly of products. Each type of drawing serves a specific purpose, and the effective use of these drawings is critical to the success of engineering and design projects. By understanding the characteristics, applications, and requirements of each type of drawing, professionals can create high-quality technical documentation that meets the needs of stakeholders. As technology continues to advance, the tools and techniques used in technical drawing will undoubtedly evolve, offering even greater precision and capabilities. However, the fundamental principles of technical drawing remain unchanged, and the ability to create precise and accurate drawings will always be a valuable skill in the engineering and design professions.
