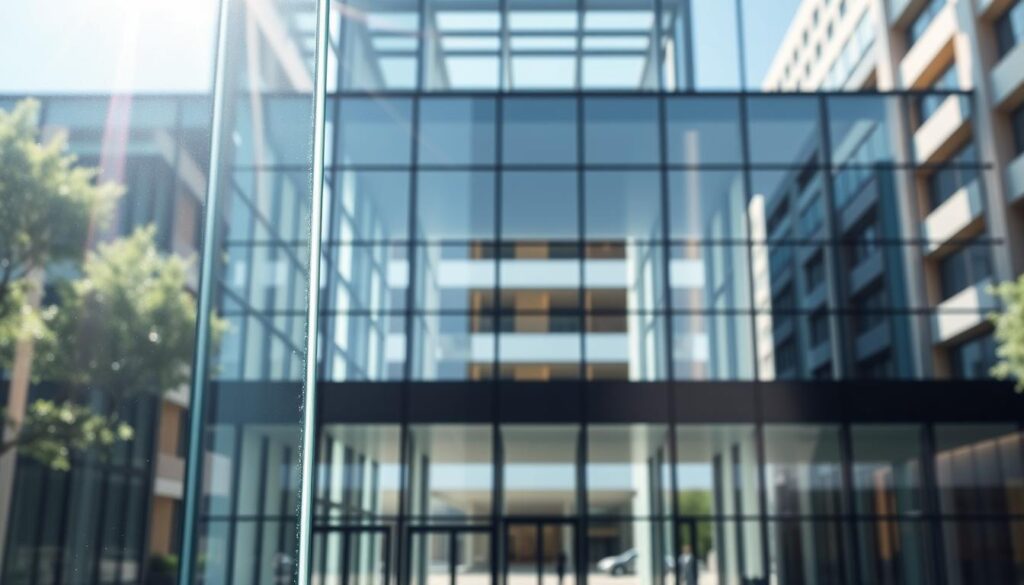
Can the right type of glass really make a difference in how we experience a building or a room? The answer lies in the technology of anti-reflective architectural glass, designed to minimize unwanted reflections and glare.
By reducing undesirable light reflection, anti-reflective glass solutions enhance transparency and provide clearer views through the glass. This not only improves the aesthetic appeal of a structure but also increases the functionality of its windows and facades.
The use of such advanced glass technology is becoming increasingly popular in modern architecture, as it offers a unique blend of form and function.
Key Takeaways
- Anti-reflective glass reduces glare and improves visibility.
- It enhances the aesthetic appeal of buildings.
- Increases the functionality of windows and facades.
- Offers a blend of form and function in modern architecture.
- Provides clearer views through the glass.
Understanding Anti-Reflective Glass
With its unique coating technology, anti-reflective glass minimizes reflections, enhancing the visual clarity of architectural structures. This advanced glass technology is becoming a staple in modern architecture due to its numerous benefits.
Definition and Characteristics
Anti-reflective glass, also known as low-reflectance building glass or non-reflective architectural glass, is designed to reduce the reflection of light on its surface. This is achieved through a specialized coating that increases light transmission and brightness, offering better contrast definition. The characteristics of anti-reflective glass make it an ideal choice for various architectural applications where visibility and aesthetics are paramount.
How Anti-Reflective Glass Works
The functionality of anti-reflective glass lies in its coating, which is typically made up of multiple layers of materials with different refractive indices. These layers work together to cancel out reflected light waves, thus reducing glare and improving visibility. For more detailed information on the technology behind anti-reflective glass, you can visit Huize Glass.
| Characteristics | Standard Glass | Anti-Reflective Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Reflection Rate | High | Low |
| Light Transmission | Moderate | High |
| Glare Reduction | No | Yes |
The table above highlights the key differences between standard glass and anti-reflective glass, showcasing the advantages of using anti-glare glass in architectural designs.
Benefits of Anti-Reflective Architectural Glass

With its advanced technology, anti-reflective architectural glass provides a multitude of benefits, including enhanced visibility, reduced glare, and improved energy efficiency. This type of glass is designed to minimize reflections and maximize the transmission of light, making it an ideal choice for various architectural applications.
Enhanced Visibility and Aesthetics
One of the primary benefits of anti-reflective glass is its ability to enhance visibility. By reducing reflections, it provides a clearer view from inside the building, making it particularly useful for commercial and residential buildings with expansive glass facades. Moreover, anti-reflective glass improves the aesthetic appeal of buildings by providing a more transparent and sleek appearance.
The enhanced visibility offered by anti-reflective glass can be particularly beneficial in environments where visual clarity is crucial, such as in retail spaces or museums. For instance, a study found that the use of anti-reflective glass in storefronts can increase customer engagement by up to 20% due to the improved visibility of products.
Reduction of Glare
Anti-reflective glass is highly effective in reducing glare, which is a common issue with traditional glass, especially in buildings with large glass surfaces. The reduction of glare not only enhances the comfort of occupants but also reduces the need for additional shading devices, thereby maintaining the architectural integrity of the building.
- Reduces eye strain caused by glare
- Minimizes the need for curtains or blinds
- Enhances the overall viewing experience
Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is another significant benefit of anti-reflective architectural glass. By allowing more natural light to enter the building, it reduces the need for artificial lighting, thereby lowering energy consumption. This is particularly beneficial in commercial buildings where lighting can account for a significant portion of energy costs.
“The use of anti-reflective glass can lead to a reduction in energy costs by up to 15% in certain building types.”
In conclusion, anti-reflective architectural glass offers a range of benefits that make it an attractive option for modern building designs. Its ability to enhance visibility, reduce glare, and improve energy efficiency makes it a valuable component in the pursuit of sustainable and aesthetically pleasing architecture.
Applications in Modern Architecture
Modern architecture has seen a significant shift towards the incorporation of anti-reflective glass, enhancing both functionality and visual appeal. This shift is evident across various types of buildings, where anti-reflective glass contributes to improved aesthetics and reduced glare.
Office Buildings
Office buildings benefit greatly from the use of anti-reflective glass. By minimizing reflections, it provides a clearer view from inside the building, enhancing the working environment. Additionally, anti-reflective glass can improve the overall appearance of the building’s facade, making it more visually appealing.
Residential Homes
In residential homes, anti-reflective glass is used to enhance the living experience. It allows for unobstructed views and reduces glare, making it ideal for homes with large windows or glass facades. Furthermore, it can help in maintaining the natural lighting within the home, reducing the need for artificial lighting.
Public Structures and Facades
Public structures, such as museums, shopping malls, and historical landmarks, also benefit from anti-reflective glass. It helps in preserving the original appearance of the structure while enhancing its visibility. For instance, in museums, it can reduce glare on exhibits, improving the visitor experience.
| Building Type | Benefits of Anti-Reflective Glass |
|---|---|
| Office Buildings | Improved working environment, enhanced facade appearance |
| Residential Homes | Unobstructed views, reduced glare, natural lighting |
| Public Structures | Preserved original appearance, enhanced visibility, improved visitor experience |
Comparing Anti-Reflective Glass to Standard Glass
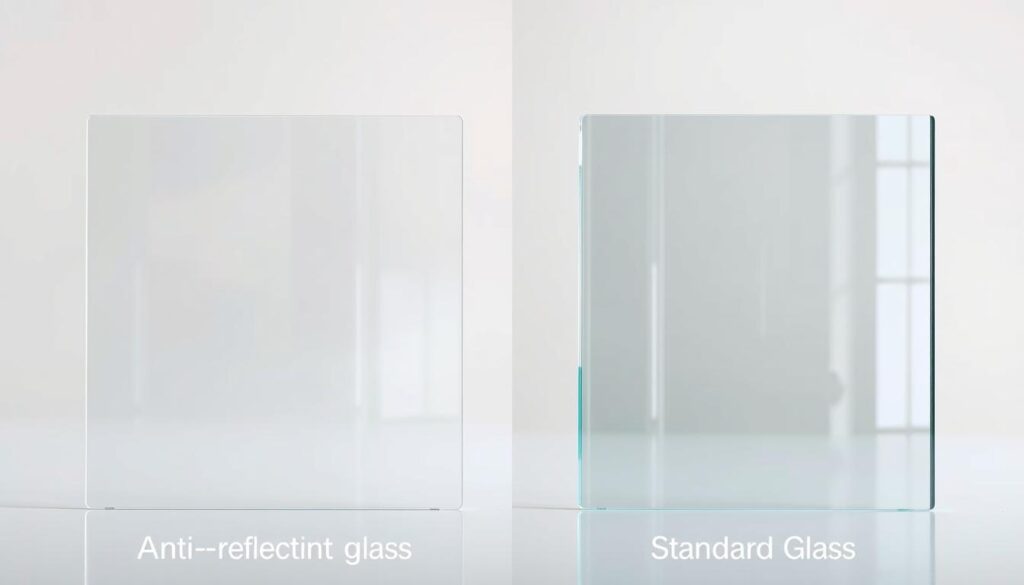

Understanding the differences between anti-reflective glass and standard glass is crucial for architects and builders looking to optimize the visibility and energy efficiency of their projects.
Anti-reflective glass is designed to minimize reflections and glare, making it an ideal choice for modern architectural designs where visibility is paramount.
Reflection Rates
One of the primary advantages of anti-reflective glass is its significantly lower reflection rate compared to standard glass. While standard glass can reflect up to 8% of light, anti-reflective glass reduces this to less than 1%.
This reduction in reflection rate not only enhances visual clarity but also improves the overall aesthetic appeal of the building.
Visual Clarity
The visual clarity offered by anti-reflective glass is substantially better than that of standard glass. By minimizing reflections, anti-reflective glass provides a clearer view, making it ideal for applications where transparency is crucial.
This is particularly beneficial in office buildings and residential homes where unobstructed views are desired.
Durability
In terms of durability, anti-reflective glass is comparable to standard glass. Both types of glass are designed to withstand various environmental conditions, including weather extremes and physical impacts.
The durability of anti-reflective glass is further enhanced by its coating, which is resistant to wear and tear.
| Characteristics | Anti-Reflective Glass | Standard Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Reflection Rate | Less than 1% | Up to 8% |
| Visual Clarity | High | Moderate |
| Durability | High | High |
As shown in the table, anti-reflective glass outperforms standard glass in terms of reflection rate and visual clarity, while both offer high durability.
The Science Behind Anti-Reflective Coatings
Understanding the science behind anti-reflective coatings is crucial for appreciating their role in modern architecture. Anti-reflective coatings are designed to reduce reflections by applying thin layers of materials with specific refractive indices.
Coating Materials and Techniques
The choice of coating materials and the techniques used to apply them are critical to the performance of anti-reflective coatings. Common materials include silicon dioxide (SiO2) and titanium dioxide (TiO2), chosen for their durability and optical properties.
The application technique typically involves a process known as magnetron sputtering, which allows for precise control over the thickness and uniformity of the coating layers.
Layer Structure and Benefits
The layer structure of anti-reflective coatings is designed to minimize reflections through a process known as destructive interference. By carefully controlling the thickness and refractive index of each layer, these coatings can significantly reduce glare and improve visibility.
The benefits of this layer structure include:
- Enhanced visual clarity
- Reduced glare
- Improved energy efficiency
| Layer Material | Refractive Index | Thickness (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 1.45 | 100 |
| TiO2 | 2.35 | 50 |
By understanding the science behind anti-reflective coatings, including the materials and techniques used, as well as the benefits of their layer structure, we can better appreciate their importance in modern architectural design.
Choosing the Right Anti-Reflective Glass

To maximize the benefits of anti-reflective glass, it’s essential to choose the right product based on specific project requirements. The decision-making process involves several key considerations that impact the performance, durability, and overall value of the glass.
Factors to Consider
When selecting anti-reflective glass, several factors come into play. These include the type of coating, which affects the glass’s reflective properties, thickness, which influences its durability and energy efficiency, and size, which impacts its applicability to different architectural designs.
The type of coating is particularly crucial as it determines the glass’s anti-reflective properties. For instance, anti-reflective glass with a high-quality coating can significantly reduce glare and improve visibility.
Thickness and Size Options
Anti-reflective glass is available in various thickness and size options to suit different architectural needs. The thickness of the glass can range from a few millimeters to several centimeters, depending on the application and the desired level of durability.
| Thickness (mm) | Size Options (m²) | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| 4-6 | 0.5-2 | Residential windows, small facades |
| 8-10 | 2-5 | Commercial buildings, larger facades |
| 12+ | 5+ | Large public structures, high-rise buildings |
In conclusion, choosing the right anti-reflective glass involves a careful consideration of various factors, including coating type, thickness, and size. By understanding these elements, architects and builders can make informed decisions that enhance the aesthetic and functional qualities of their projects.
Cost Implications of Anti-Reflective Glass
Understanding the financial aspects of anti-reflective glass is crucial for architects and builders looking to incorporate this technology into their projects. While anti-reflective glass offers numerous benefits, including energy efficiency and enhanced aesthetics, its cost implications are a significant consideration.
Initial Investment vs. Long-Term Savings
The initial investment in anti-reflective glass is often higher compared to standard glass. However, this initial cost is offset by the long-term savings it provides. For instance, anti-reflective glass can significantly reduce energy consumption by minimizing the need for artificial lighting and optimizing natural light usage. According to a report by imarcgroup, the energy efficiency of anti-reflective glass can lead to substantial savings over time.
Key benefits of anti-reflective glass include:
- Reduced energy consumption
- Lower maintenance costs due to its durable coating
- Enhanced property value through improved aesthetics
As Andrew Watts, a renowned architect, once noted, “The long-term benefits of anti-reflective glass far outweigh the initial costs, making it a wise investment for sustainable building practices.”
Pricing Factors
Several factors influence the pricing of anti-reflective glass, including the type of coating used, the size of the glass panels, and the complexity of the installation process. Additionally, the manufacturing process and the technology employed can also impact the final cost. It’s essential for builders and architects to consider these factors when budgeting for anti-reflective glass.
“The cost of anti-reflective glass is not just about the initial price; it’s about understanding the value it brings to a building’s overall efficiency and appeal.” –
By carefully evaluating the cost implications and considering the long-term benefits, architects and builders can make informed decisions about incorporating anti-reflective glass into their projects.
Installation Process for Anti-Reflective Glass

Proper installation is key to maximizing the benefits of anti-reflective glass in architectural projects. The process involves several critical steps that ensure the glass performs optimally and provides the desired aesthetic and functional benefits.
Site Preparation
Before the installation of anti-reflective glass, thorough site preparation is crucial. This involves assessing the site conditions, ensuring that the frames and structures are ready for the glass, and that all necessary tools and equipment are available.
Key steps in site preparation include:
- Inspecting the site for any potential hazards or obstacles
- Ensuring that the frames are correctly aligned and securely fixed
- Cleaning the area where the glass will be installed
For detailed guidelines on preparing the site, refer to the Guardian Glass processing guidelines.
Professional Installation vs. DIY
When it comes to installing anti-reflective glass, the decision between hiring professionals and attempting a DIY installation is crucial. While DIY might seem cost-effective, professional installation ensures that the glass is installed correctly, minimizing the risk of damage or improper fitting.
“Professional installation of anti-reflective glass not only ensures optimal performance but also extends the lifespan of the glass by minimizing potential damages during the installation process.”
A comparison between professional installation and DIY is illustrated in the table below:
| Aspect | Professional Installation | DIY Installation |
|---|---|---|
| Expertise | Highly skilled professionals | Varies based on individual’s skill level |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost | Lower upfront cost, potential for additional costs due to mistakes |
| Quality of Work | Guaranteed quality and warranty | Dependent on individual’s expertise |
In conclusion, while the initial cost of professional installation may be higher, the long-term benefits and reduced risk of errors make it the preferred choice for installing anti-reflective glass.
Maintenance of Anti-Reflective Glass
To keep anti-reflective glass performing at its best, regular maintenance is essential. This involves understanding the proper cleaning techniques and being aware of common issues that may arise.
Cleaning Guidelines
Regular cleaning with appropriate materials is crucial for maintaining the effectiveness of anti-reflective glass. It’s recommended to use a soft, dry cloth to wipe away dust and debris. For more thorough cleaning, a mild soap solution can be used, but avoid harsh chemicals or abrasive materials that could damage the coating.
For stubborn stains or dirt buildup, consider the following steps:
- Mix a solution of mild soap and warm water.
- Dip a soft cloth into the solution, wring it out thoroughly, and wipe the glass gently.
- Rinse the cloth with clean water, wring it out again, and wipe the glass to remove any soap residue.
- Dry the glass with a clean, dry cloth to prevent water spots.
Common Issues and Solutions
Despite proper cleaning, anti-reflective glass can sometimes encounter issues such as streaks, spots, or damage to the coating. For streaks and spots, ensure that the cleaning cloth is clean and free of debris. If the issue persists, consider using a specialized glass cleaner designed for anti-reflective coatings.
In cases where the coating is damaged, it’s essential to assess the extent of the damage. Minor scratches may not significantly impact performance, but deep scratches or large areas of damage may require professional repair or replacement.
To prevent damage, consider the following tips:
- Avoid using sharp objects near the glass.
- Keep the glass clean to prevent dirt buildup.
- Use protective coverings during construction or renovation phases.
Environmental Impact of Anti-Reflective Glass
The environmental benefits of anti-reflective glass are multifaceted, ranging from sustainable manufacturing to enhanced energy efficiency in buildings. As the construction industry continues to evolve, understanding the ecological footprint of materials like anti-reflective glass is crucial.
Anti-reflective glass contributes to a reduction in environmental impact through its manufacturing process and its role in building energy efficiency. By minimizing glare and maximizing natural light transmission, it reduces the need for artificial lighting, thereby lowering energy consumption.
Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
Manufacturers are increasingly adopting sustainable manufacturing practices to reduce the environmental footprint of anti-reflective glass. This includes using recycled materials, minimizing waste, and optimizing production processes to consume less energy. For instance, some manufacturers are now incorporating recycled glass into their production lines, significantly reducing the need for raw materials and lowering greenhouse gas emissions.
For more information on sustainable building materials, visit https://worldcivilsociety.com/sustainable-building-materials/.
| Manufacturing Aspect | Traditional Method | Sustainable Practice |
|---|---|---|
| Material Sourcing | Raw materials | Recycled glass content |
| Energy Consumption | High energy usage | Energy-efficient processes |
| Waste Management | Significant waste generation | Minimal waste through recycling |
Energy Savings in Buildings
Anti-reflective glass plays a significant role in achieving energy savings in buildings. By enhancing natural light transmission, it reduces the reliance on artificial lighting systems, which are among the largest consumers of electricity in commercial and residential buildings. This not only lowers energy bills but also contributes to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions associated with energy production.
A study on energy-efficient buildings highlighted that the use of anti-reflective glass can lead to significant energy savings, often cited in the range of 10-20% depending on the building’s design and location. This makes anti-reflective glass an attractive option for architects and builders looking to create more sustainable and energy-efficient structures.
Case Studies of Anti-Reflective Glass Implementations
The implementation of anti-reflective glass in various buildings has demonstrated its effectiveness in reducing glare and improving aesthetics. Case studies of anti-reflective glass implementations reveal the significant impact it has on both the functionality and visual appeal of buildings.
Several architectural projects have successfully integrated anti-reflective glass, showcasing its potential in modern construction. These projects not only highlight the benefits of anti-reflective glass but also provide valuable insights into its applications and challenges.
Notable Architectural Projects
One notable example is the Apple Store in New York City, which features a stunning glass cube designed by Steve Jobs and Norman Foster. The use of anti-reflective glass in this project minimized reflections, providing an unobstructed view of the store’s interior.
Another example is the VanDusen Botanical Garden Visitor Centre in Vancouver, Canada. This building incorporated anti-reflective glass to reduce glare and enhance the overall visitor experience. The glass helped to create a seamless transition between the indoors and outdoors.
| Project | Location | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Apple Store | New York City, USA | Minimized reflections, enhanced visibility |
| VanDusen Botanical Garden Visitor Centre | Vancouver, Canada | Reduced glare, improved visitor experience |
| Google Headquarters | Mountain View, USA | Energy efficiency, aesthetic appeal |
Lessons Learned
The case studies of these notable architectural projects provide valuable lessons for future implementations. One key takeaway is the importance of considering the angle of incidence to minimize reflections. Additionally, the durability of anti-reflective coatings has been a significant factor in the long-term success of these projects.
Proper installation and maintenance are also crucial to ensuring the longevity and effectiveness of anti-reflective glass. By understanding these factors, architects and builders can better design and implement anti-reflective glass in their projects.
Future Trends in Architectural Glass

The future of architectural glass is poised to be shaped by innovations in anti-reflective technology. As the demand for energy-efficient and aesthetically pleasing buildings continues to grow, the role of advanced glass technologies becomes increasingly significant.
Innovations in Anti-Reflective Technology
Recent advancements in anti-reflective coatings have led to the development of more efficient and durable glass products. These innovations are crucial in reducing glare and improving visual clarity, making buildings more comfortable and energy-efficient. Some of the key innovations include:
- Advanced nanotechnology-based coatings that minimize reflection
- Multi-layer coatings that enhance durability and performance
- Smart glass technologies that adjust to environmental conditions
For a deeper dive into the design and application of structural glass, visit our comprehensive guide on structural glass design.
Market Predictions
The market for anti-reflective glass is expected to grow significantly, driven by the increasing demand for sustainable and energy-efficient building solutions. Key factors influencing this growth include:
- Rising awareness of energy conservation and environmental sustainability
- Government regulations and incentives promoting green building practices
- Technological advancements in glass manufacturing and coating techniques
Market analysts predict that the adoption of anti-reflective glass will become more widespread across various sectors, including residential, commercial, and public buildings. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of anti-reflective glass in the future.
Regulatory Standards for Architectural Glass
Architectural glass, including anti-reflective glass, is subject to various regulatory standards that ensure its safety and performance in buildings. These standards are crucial for guaranteeing that glass installations meet the necessary criteria for safety, durability, and energy efficiency.
Safety Regulations
Safety regulations are a critical component of the regulatory framework governing architectural glass. These regulations are designed to prevent injuries and ensure that glass installations do not pose a hazard to occupants. For instance, the Consumer Product Safety Commission’s regulations on architectural glazing materials outline specific safety standards that must be met.
Some of the key safety regulations include:
- Requirements for impact resistance to prevent shattering upon impact.
- Standards for labeling and identification to ensure that products are traceable and compliant.
- Guidelines for safe installation practices to minimize the risk of injury during and after installation.
As emphasized by industry experts, “Compliance with safety regulations is not just a legal requirement but a moral obligation to ensure the well-being of building occupants.”
Performance Standards
Performance standards for architectural glass cover aspects such as thermal performance, optical quality, and durability. These standards help architects and builders select glass products that meet their project’s specific needs while ensuring energy efficiency and occupant comfort.
Some key performance standards include:
- Energy efficiency ratings to minimize heat transfer and reduce energy consumption.
- Optical performance metrics, such as visible light transmittance and reflectance, to optimize daylighting and reduce glare.
- Durability tests to ensure that glass products can withstand environmental stresses over their lifespan.
“The selection of architectural glass that meets performance standards is crucial for creating sustainable and comfortable buildings,” notes a leading architectural firm.
Conclusion: The Future of Visibility in Architecture
Anti-reflective glass is revolutionizing the architectural landscape by enhancing visibility and contributing to sustainable design. With its ability to reduce glare and improve light transmission, this technology is becoming increasingly vital in modern building design.
Key Advantages
The benefits of anti-reflective glass include unparalleled optical performance, durability, and environmental sustainability. AGC’s AR coating technology, for instance, boasts a residual reflection below 0.5% across UV to IR wavelengths, ensuring superior optical performance. This technology is applied in various architectural projects, from office buildings to residential homes, to enhance energy efficiency and aesthetics.
Sustainable Design Implications
By reducing the need for artificial lighting and improving energy efficiency, anti-reflective glass plays a significant role in sustainable architectural design. As the industry continues to evolve, innovations in anti-reflective technology will be crucial in shaping the future of visibility in architecture. For more information on AGC’s anti-reflective coatings, visit their website to explore the technical details and applications.
